General Dynamics FGR-17 Viper
The Viper was man-portable unguided line-of-sight antitank 70 mm rocket developed as a successor to the U.S. Army's 66 mm M72 LAW (Lightweight Antitank Weapon) system.
In 1975, a replacement program for the LAW was initiated under the name ILAW (Improved LAW), with General Dynamics as prime contractor. The name was subsequently changed to Viper in January 1976, and the designation XFGR-17A was assigned. The allocation of an MDS rocket designator to this weapon is remarkable, because such nomenclature is usually not assigned to unguided line-of-sight rockets.
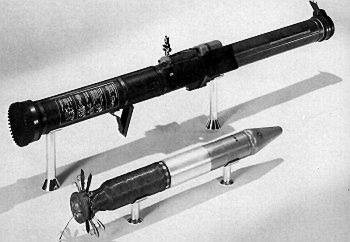 |
| Photo: General Dynamics |
| XFGR-17A |
In August 1981, production of the XM132 Viper rocket (possibly designated FGR-17A, but I have no confirmation for this) was approved, and it was planned to procure up to 90000 Viper rockets for the U.S. Army. This was not to be, however, because in October 1983, the whole Viper program was cancelled. The weapon reportedly was much more expensive than originally expected, and also had some safety (sensitivity to static electricity) and performance problems. In place of the Viper, the U.S. Army purchased the Swedish AT4 recoilless rifle as the M136 LMPW (Light Multi-Purpose Weapon).
Specifications
Note: Data given by several sources show slight variations. Figures given below may therefore be inaccurate!
Data for XFGR-17A:
| Length | 0.7 m (27 in) |
| Diameter | 70 mm (2.75 in) |
| Weight | 3.73 kg (8.23 lb) |
| Speed | 257 m/s (843 ft/s) |
| Range | 250 m (820 ft) |
| Propulsion | Solid rocket |
| Warhead | High explosive |
Main Sources
[1] Redstone Arsenal Historical Information Website
Back to Current Designations Of U.S. Unmanned Military Aerospace Vehicles
Back to
Directory of U.S. Military Rockets and Missiles
Last Updated: 12 September 2006