Atlantic Research MQR-16 Gunrunner
The Gunrunner was a low-cost expendable ballistic aerial target system for air-defense weapon training. It was developed in the late 1960s mainly for use in Army and Navy training with the FIM-43 Redeye man-portable surface-to-air missiles, and entered service in 1969. In March 1971, the designation MQR-16A was assigned to Gunrunner.
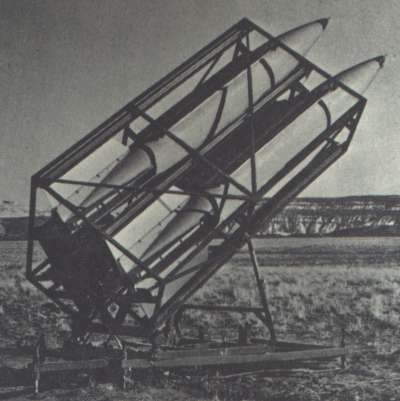 |
| Photo: via National Aerospace Education Council |
| MQR-16A |
The MQR-16A was of simple and light-weight construction, using plywood fins and readily available HVAR (High Velocity Aerial Rocket) motors for propulsion. It carried an IR source in the nose to make lock-on by the FIM-43 Redeye missile possible. For a high launch rate, the Gunrunner was launched from a three-rocket launcher with adjustable elevation and azimuth. The target was probably phased out of service at some time in the late 1980s.
Specifications
Note: Data given by several sources show slight variations. Figures given below may therefore be inaccurate!
Data for MQR-16A:
| Length | 4.88 m (16 ft) |
| Diameter | 0.51 m (20 in) |
| Weight | 131 kg (290 lb) |
| Speed | 930 km/h (500 kts) |
| Range | 4900 m (16000 ft) |
| Flight Time | 10-33 s |
| Propulsion | Booster: HVAR (0.86ES5800) solid-fuel rocket; 26 kN (5800 lb) for 0.86 s Sustainer: 10KS300 solid-fuel rocket; 1.3 kN (300 lb) for 10 s |
Main Sources
[1] James J. Haggerty (ed.): "1970 United States Aircraft, Missiles and Spacecraft", National Aerospace Education Council, 1970
[2] Department of Defense Missile Nomenclature Records
Back to Current Designations Of U.S. Unmanned Military Aerospace Vehicles
Back to
Directory of U.S. Military Rockets and Missiles
Last Updated: 22 October 2002