Lockheed Martin (LTV) MGM-140 ATACMS
The ATACMS (Army Tactical Missile System) is the U.S. Army's current short/medium-range tactical ballistic missile system. Development began in 1982, when the DOD combined the Army's CSWS (Corps Support Weapon System, started in 1980 as a successor to MGM-52 Lance) and the Air Force's CSW (Conventional Standoff Weapon) programs into the JTACMS (Joint Tactical Missile System) program. In 1985, after pre-development contracts had been awarded to several companies, the USAF pulled out of the program, and JTACMS was renamed ATACMS.
In May 1986 the prime contract for development of ATACMS was awarded to Ling-Temco-Vought (LTV), and shortly thereafter, the missile designator MGM-140 was assigned. The first flight of an XMGM-140A missile occurred in April 1988, and in December of that year, low-rate production started. The MGM-140A ATACMS became operational in January 1991, and began to replace the MGM-52 Lance SRBM. In U.S. Army service, the complete ATACMS missile round including the launch pod is known as M39. LTV's missile division was aquired by Loral in 1992, forming Loral Vought Systems, which was in turn purchased by Lockheed Martin in 1996. The current prime contractor for ATACMS is Lockheed Martin Missiles and Fire Control.
 |
| Photo: U.S. Army |
| XMGM-140A |
The MGM-140A, also known as ATACMS Block I, is powered by a single-stage solid-fuel rocket motor, and is guided to the target by a ring-laser gyro based inertial system. The warhead section consists of 950 M74 anti-personnel/anti-materiel (APAM) bomblets, which are distributed over an area of 33000 m2 (360000 sq.ft). The missile is launched from an M270 MLRS (Multiple Launch Rocket System) launcher, and maximum range is about 165 km (100 miles). The ATACMS is tasked primarily with the destruction of tactical surface-to-surface missile sites, air defense sites, and C3 (Command, Control and Communications) complexes. 32 MGM-140A missiles were fired in Operation Desert Storm against Iraqi targets.
 |
| Photo: Lockheed Martin |
| MGM-140A |
In 1992 the design of an improved missile was begun, designated MGM-140B ATACMS Block IA. The MGM-140B includes GPS in its guidance system, which significantly increases accuracy at long ranges. To fully exploit this new feature, the warhead weight was reduced and only 275 M74 bomblets are carried, increasing the range to 300 km (185 miles). The first XMGM-140B test flight occurred in October 1994, and the MGM-140B entered service in 1998.
The designation MGM-140C was originally allocated to the ATACMS Block II, which carried the Northrop Grumman BAT (Brilliant Anti-Tank) guided submunition. The production variant of the MGM-140C, which included improvements made under the so-called "TACMS 2000" (T2K) program, had been designated as MGM-164A, q.v. for further information. The ATACMS Block II program was terminated in late 2003.
The MGM-140D is described by source [4] as an "upgraded missile with numerous structural improvements." Most probably, this refers to an upgrade of the MGM-140B ATACMS Block IA.
The ATACMS Block IVA, originally known as Block IA Unitary and designated MGM-140E, has also been subject to the T2K improvement program. It is now built as the MGM-168A, q.v. for further information.
In January 2003 the designation MGM-140F was allocated to a new ATACMS variant or upgrade, but currently no details on the MGM-140F are available.
ATACMS Block III was a projected hard-target penetrator version with a planned range of about 220 km. The Block III, also known as TACMS-P (P = Penetrator), was funded as an ACTD (Advanced Concept Technology Demonstration) program since 2001, and the first flight of a TACMS-P prototype occured in March 2004. The program was subsequently terminated.
A ship-launched ATACMS variant for the U.S. Navy (called NATACMS) was also under development, but has been cancelled.
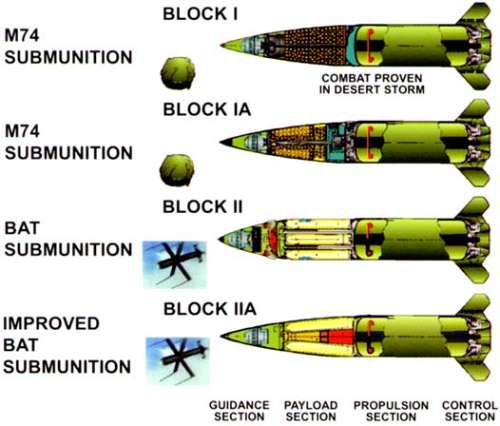 |
| Image: Lockheed Martin |
| MGM-140 / MGM-164 ATACMS variants |
Until March 2002, more than 1600 MGM-140A and 500 MGM-140B missiles have been built. Current ATACMS production versions include the MGM-140B and MGM-168A.
Specifications
Note: Data given by several sources show slight variations. Figures given below may therefore be inaccurate!
Data for MGM-140A (except where noted):
| Length | 4.0 m (13 ft) |
| Diameter | 0.61 m (24 in) |
| Finspan | 1.4 m (55 in) |
| Weight | 1670 kg (3690 lb); MGM-140B: 1320 kg (2910 lb); MGM-140C (MGM-164A): 1480 kg (3270 lb) |
| Ceiling | > 50 km (30 miles) |
| Range | 165 km (102 miles); MGM-140B/E: 300 km (186 miles); MGM-140C (MGM-164A): 140 km (87 miles) |
| Propulsion | Solid-fueled rocket |
| Warhead | 560 kg (1240 lb) (950 M74 APAM bomblets); MGM-140B: 160 kg (353 lb) (275 M74 APAM bomblets); MGM-140C (MGM-164A): 268 kg (592 lb) (13 BAT submunitions); MGM-140E (MGM-168A): 227 kg (500 lb) WAU-23/B unitary high-explosive |
Main Sources
[1] Hajime Ozu: "Missile 2000 - Reference Guide to World Missile Systems", Shinkigensha, 2000
[2] Redstone Arsenal Historical Information Website
[3] Lockheed Martin Missiles and Fire Control Website
[4] Department of Defense Missile Nomenclature Records
Back to Current Designations Of U.S. Unmanned Military Aerospace Vehicles
Back to Directory of U.S. Military Rockets and Missiles
Last Updated: 19 September 2006