Boeing (Rockwell) NS-7 Navstar GPS
GPS Block I
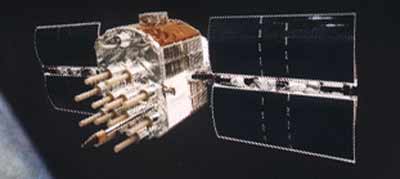
The designation NS-7A referred to the Navstar series of navigational satellite also known as Navigational Development Satellite (NDS) and the Global Positioning System (GPS). The satellites were developed for the US Navy by Rockwell and four satellites provided a positional fix with an accuracy of 30 m. It was also made available to civilian users. The 525 kg Navstar satellites were fitted with three rubidium clocks and one caesium clock. They transmitted at 1575.42 MHz for civilian users and at 1227.6 MHz for military users.
 |
| Image: Author's collection |
| NS-7A Navstar-1 (1978-020A) |
| Name | Intl. Designation | Launch | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Navstar-1 | 1978-020A | 22-Feb-1978 | Also known as Ops-5111 |
| Navstar-2 | 1978-047A | 13-May-1978 | Also known as Ops-5112 |
| Navstar-3 | 1978-093A | 7-Oct-1978 | Also known as Ops-5113 |
| Navstar-4 | 1978-112A | 11-Dec-1978 | Also known as Ops-5114 |
| Navstar-5 | 1980-011A | 9-Feb-1980 | Also known as Ops-5117 |
| Navstar-6 | 1980-032A | 26-Apr-1980 | Also known as Ops-5118 |
| Navstar-7 | --- | 18-Dec-1981 | Failed to orbit |
| Navstar-8 | 1983-072A | 14-Jul-1983 | Also known as Ops-9794 |
| Navstar-9 | 1984-059A | 13-Jun-1984 | Also known as USA-1 |
| Navstar-10 | 1984-097A | 8-Sep-1984 | Also known as USA-5 |
| Navstar-11 | 1985-093A | 9-Oct-1985 | Also known as USA-10 |
Launch dates of the Navstar series
GPS Block II
The Navstar 2 system, designated as NS-7B, was also built by Rockwell. The operational system consisted of 21 satellites. Each 1665 kg satellite was equipped with an atomic clock with an accuracy of 1 second in 300,000 years. The transmissions were at 1575.42 MHz for civilian purposes and 1227.6 MHz for military purposes.
 |
| Image: Author's collection |
| NS-7B Navstar 2-1 (1989-013A) |
| Name | Intl. Designation | Launch | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Navstar 2-1 | 1989-013A | 14-Feb-1989 | Also known as USA-35 |
| Navstar 2-2 | 1989-044A | 10-Jun-1989 | Also known as USA-38 |
| Navstar 2-3 | 1989-064A | 18-Aug-1989 | Also known as USA-42 |
| Navstar 2-4 | 1989-085A | 21-Oct-1989 | Also known as USA-47 |
| Navstar 2-5 | 1989-097A | 11-Dec-1989 | Also known as USA-49 |
| Navstar 2-6 | 1990-008A | 24-Jan-1990 | Also known as USA-50 |
| Navstar 2-7 | 1990-025A | 26-Mar-1990 | Also known as USA-54 |
| Navstar 2-8 | 1990-068A | 2-Aug-1990 | Also known as USA-63 |
| Navstar 2-9 | 1990-088A | 1-Oct-1990 | Also known as USA-64 |
Launch dates of the Navstar 2 series
The Navstar 2A series, designated as NS-7C, was similar to the Navstar 2 series but carried improved instrumentation.
| Name | Intl. Designation | Launch | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Navstar 2A-1 | 1990-103A | 26-Nov-1990 | Also known as USA-66 |
| Navstar 2A-2 | 1991-047A | 4-Jul-1991 | Also known as USA-71 |
| Navstar 2A-3 | 1992-009A | 23-Feb-1992 | Also known as USA-79 |
| Navstar 2A-4 | 1992-019A | 10-Apr-1992 | Also known as USA-80 |
| Navstar 2A-5 | 1992-039A | 7-Jul-1992 | Also known as USA-83 |
| Navstar 2A-6 | 1992-058A | 9-Sep-1992 | Also known as USA-84 |
| Navstar 2A-7 | 1992-079A | 23-Nov-1992 | Also known as USA-85 |
| Navstar 2A-8 | 1992-089A | 18-Dec-1992 | Also known as USA-87 |
| Navstar 2A-9 | 1993-007A | 3-Feb-1993 | Also known as USA-88 |
| Navstar 2A-10 | 1993-017A | 30-Mar-1993 | Also known as USA-90 |
| Navstar 2A-11 | 1993-032A | 13-May-1993 | Also known as USA-91 |
| Navstar 2A-12 | 1993-042A | 26-Jun-1993 | Also known as USA-92 |
| Navstar 2A-13 | 1993-054A | 30-Aug-1993 | Also known as USA-94 |
| Navstar 2A-14 | 1993-068A | 26-Oct-1993 | Also known as USA-96 |
| Navstar 2A-15 | 1994-016A | 10-Mar-1994 | Also known as USA-100 |
| Navstar 2A-16 | 1996-019A | 28-Mar-1996 | Also known as USA-117 |
| Navstar 2A-17 | 1996-041A | 16-Jul-1996 | Also known as USA-126 |
| Navstar 2A-18 | 1996-056A | 12-Sep-1996 | Also known as USA-128 |
| Navstar 2A-19 | 1997-067A | 5-Nov-1997 | Also known as USA-134 |
Launch dates of the Navstar 2A series
Further improvements to the instrumentation was introduced with the Navstar 2R ("R" for "replenishment") series, which was also designated as NS-7D. Whilst these satellites used the original Rockwell design, they were in fact built by Lockheed Martin. Navstar 2R-M was a "modernised" version (hence the "M") of the 2R series. The series used the remaining eight unlaunched 2R satellites but converted with increased power for existing signals and two new military signals as well as a second civilian signal, along with a redesigned external antenna panel and more efficient transmitters. The mass of the satellites increased by 28 kg to 2073 kg.
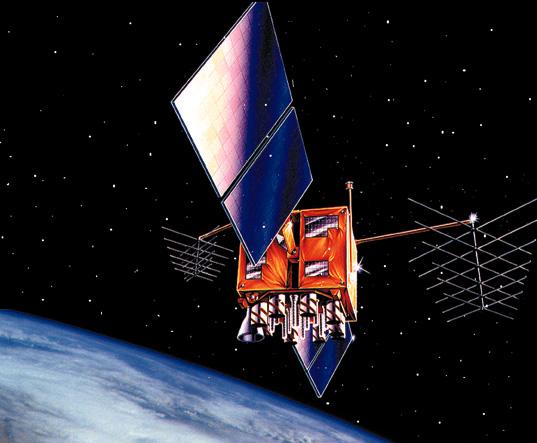 |
| Image: Lockheed Martin |
| NS-7D |
| Name | Intl. Designation | Launch | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| GPS 2R-1 | --- | 17-Jan-1997 | Failed to orbit |
| GPS 2R-2 | 1997-035A | 23-Jul-1997 | Also known as USA-132 |
| GPS 2R-3 | 1999-055A | 7-Oct-1999 | Also known as USA-145 |
| GPS 2R-4 | 2000-025A | 11-May-2000 | Also known as USA-150 |
| GPS 2R-5 | 2000-040A | 16-Jul-2000 | Also known as USA-151 |
| GPS 2R-6 | 2000-071A | 10-Nov-2000 | Also known as USA-154 |
| GPS 2R-7 | 2001-004A | 30-Jan-2001 | Also known as USA-156 |
| GPS 2R-8 | 2003-005A | 29-Jan-2003 | Also known as USA-166 |
| GPS 2R-9 | 2003-010A | 31-Mar-2003 | Also known as USA-168 |
| GPS 2R-10 | 2003-058A | 21-Dec-2003 | Also known as USA-175 |
| GPS 2R-11 | 2004-009A | 20-Mar-2004 | Also known as USA-177 |
| GPS 2R-12 | 2004-023A | 23-Jun-2004 | Also known as USA-178 |
| GPS 2R-13 | 2004-045A | 6-Nov-2004 | Also known as USA-180 |
| GPS 2RM-1 | 2005-038A | 26-Sep-2005 | ex GPS-2R-14; also known as USA-183 |
| GPS 2RM-2 | 2006-042A | 26-Sep-2006 | ex GPS-2R-15; also known as USA-190 |
| GPS 2RM-3 | 2006-052A | 17-Nov-2005 | ex GPS-2R-16; also known as USA-192 |
| GPS 2RM-4 | 2007-047A | 17-Oct-2007 | ex GPS-2R-17; also known as USA-196 |
| GPS 2RM-5 | 2007-062A | 20-Dec-2007 | ex GPS-2R-18; also known as USA-199 |
| GPS 2RM-6 | 2008-012A | 15-Mar-2008 | ex GPS-2R-19; also known as USA-201 |
| GPS 2RM-7 | 2009-014A | 24-Mar-2009 | ex GPS-2R-20; also known as USA-203 |
| GPS 2RM-8 | 2009-043A | 07-Aug-2009 | ex GPS-2R-21; also known as USA-206 |
Launch dates of the GPS 2R (Navstar 2R) series
The designation NS-7E refers to the Navstar 2F series of satellites. Boeing (which now owns Rockwell) has received an order to build six against a requirement of 33 by 2012. As it is recognised that over the years that the Navstar 2F series will be launched, technology and needs will change, Boeing has adopted a modular approach which will allow them to meet those changes.
 |
| Image: Boeing |
| NS-7E |
| Name | Intl. Designation | Launch | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| GPS 2F-1 | 2010-022A | 28-May-2010 | Also known as USA-213 |
| GPS 2F-2 | 2011-036A | 16-Jul-2011 | Also known as USA-232 |
| GPS 2F-3 | 2012-053A | 04-Oct-2012 | Also known as USA-239 |
| GPS 2F-4 | 2013-023A | 15-May-2013 | Also known as USA-242 |
| GPS 2F-5 | 2014-008A | 21-Feb-2014 | Also known as USA-248 |
| GPS 2F-6 | 2014-026A | 17-May-2014 | Also known as USA-251 |
| GPS 2F-7 | 2014-045A | 02-Aug-2014 | Also known as USA-256 |
| GPS 2F-8 | 2014-068A | 29-Oct-2014 | Also known as USA-258 |
| GPS 2F-9 | 2015-013A | 25-Mar-2015 | Also known as USA-260 |
| GPS 2F-10 | 2015-033A | 15-Jul-2015 | Also known as USA-262 |
| GPS 2F-11 | 2015-062A | 31-Oct-2015 | Also known as USA-265 |
| GPS 2F-12 | 2016-007A | 05-Feb-2016 | Also known as USA-266 |
Launch dates of the GPS 2F (Navstar 2F) series
GPS Block III
The third generation of GPS satellites is known as GPS Block III or simply GPS 3. Prime contractor is Lockheed Martin, building on their experience with the GPS 2R series. A total of 10 GPS Block III satellites is on order. A major improvement of the GPS 3 satellites are new navigation signals to increase availability and accuracy for civilian and military users. Additionally, the satellites have a directional antenna to transmit the latest military signal standard (called M-Code) with high power to a specific area on Earth.
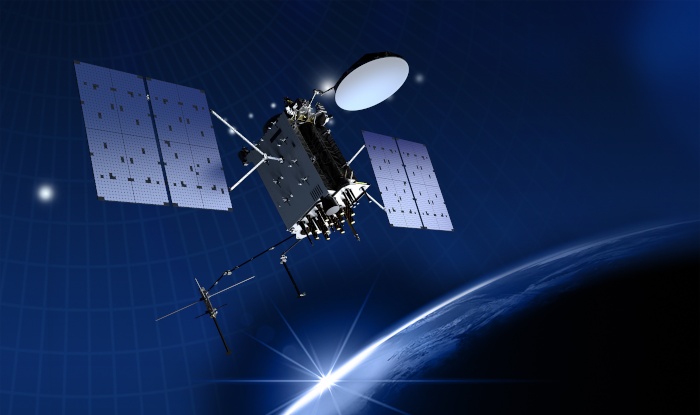 |
| Image: Lockheed Martin / USSF |
| GPS Block III |
| Name | Intl. Designation | Launch | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| GPS 3-1 | 2018-109A | 23-Dec-2018 | Also known as USA-289 |
| GPS 3-2 | 2019-056A | 22-Aug-2019 | Also known as USA-293 |
| GPS 3-3 | 2020-041A | 30-Jun-2020 | Also known as USA-304 |
| GPS 3-4 | 2020-078A | 05-Nov-2020 | Also known as USA-309 |
| GPS 3-5 | 2021-054A | 17-Jun-2021 | Also known as USA-319 |
| GPS 3-6 | 2023-009A | 18-Jan-2023 | Also known as USA-343 |
Launch dates of the GPS 3 (Navstar 3) series
After the 10 Block III satellites, production will switch to the further improved Block IIIF. Current plans call for the launch of 22 Block IIIF satellites.
Background history
Navigational satellites are essentially radio transmitters of which the orbital positions are known. Through analysing the signals from three satellites, a navigator is not only able to determine his longitude and latitude but also, where appropriate, his altitude.
The early navigational satellites in the Transit series used a radio-Doppler navigation method in which the ship's position was calculated from the observed change in the received frequency of the satellite radio transmission as the satellite passes across the sky. This technique is based on the principle that the orbit of a satellite can be accurately computed by the analysis of the Doppler shift of the radio transmissions by the satellites. The accuracy is, however, limited by the frequency stability of the satellite transmissions and the ability to predict the satellite's orbit between the time it is measured by a ground tracking station and the time the user observed the satellite.
Another method is based on time ranging. Here the user calculates his distance from a satellite by a measurement of the time that the radio signal of the satellite takes to cover the distance to the receiver. To achieve a reasonable accuracy, this method requires three separate satellites and a very accurate clock.
Transit series
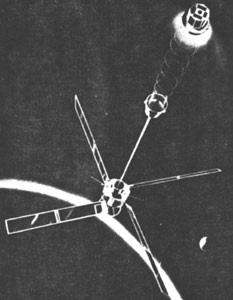
The early navigational satellites of the United States were of an experimental nature. They were sponsored by the U.S. Navy and were built by RCA. The Transit-1A and -2 series carried two ultrastable oscillators, an electronic clock and four frequency transmitters which operated in the 162/216 MHz and 53/324 MHz bands. Transit-3 carried in addition a small magnetic memory. The Transit-4 series, which was of a different design, was unique in that they carried a Supplementary Nuclear Power (SNAP) source to generate the satellite's power requirements. Transmitters operated at 150/400 MHz. The Transit-5 series satellites were of an octagonal shape and carried dual frequency transmitters as well as a 30 m gravity gradient stabilisation boom. The 5A sub-series were powered by solar cells whilst the 5B sub-series carried a SNAP-9A nuclear power source. The 5C sub-series reverted again to solar cells.
 |
| Image: Author's collection |
| Transit-5C1 (1964-026A) |
| Name | Intl. Designation | Launch | Re-entry | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Transit-1A | --- | 17-Sep-1959 | --- | Failed to orbit |
| Transit-1B | 1960 γ2 | 13-Apr-1960 | 5-Oct-1967 | |
| Transit-2A | 1960 η1 | 22-Jun-1960 | ||
| Transit-3A | --- | 30-Nov-1960 | --- | Failed to orbit |
| Transit-3B | 1961 η1 | 21-Feb-1961 | 30-Mar-1961 | Failed to separate from Lofti-1 |
| Transit-4A | 1961 ο1 | 29-Jun-1961 | ||
| Transit-4B | 1961 αη1 | 15-Nov-1961 | ||
| Transit-5A1 | 1962 βψ1 | 19-Dec-1962 | 25-Sep-1986 | |
| Transit-5A2 | --- | 5-Apr-1963 | --- | Also known as Ops-0804; failed to orbit |
| Transit-5A3 | 1963-022A | 16-Jun-1963 | 3-Aug-1990 | |
| Transit-5BN1 | 1963-038B | 28-Sep-1963 | ||
| Transit-5BN2 | 1963-049B | 5-Dec-1963 | ||
| Transit-5BN3 | --- | 21-Apr-1964 | --- | Failed to orbit |
| Transit-5C1 | 1964-026A | 4-Jun-1964 | Also known as Ops-4412 |
Launch dates of the Transit series
NNSS
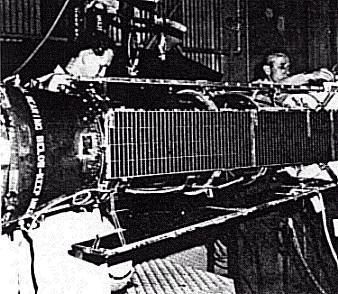
The Navy Navigational Satellite System (NNSS), also called Oscar or Transit-O, was the first operational system. The principal objective was to provide positioning facilities with an accuracy of 150 m to submarines carrying Polaris missiles. At a later stage the system was also made available to civilian users. The satellites transmitted at 150 MHz and 400 MHz. Whilst six satellites provide a useful coverage, additional satellites have been launched as in-orbit spares. The satellites had an initial mass of 32 kg and in total 32 were built by RCA. They have been identified by the third and fourth characters in the numeric designation whilst the meaning of the numeric '3' is not known.
A number of the satellites were converted for other uses as Transat (#11), P76-5 (#15), Hilat (#16) and Polar Bear (#17). Spacecraft #22 was used in 1992 ground tests to assess the impact of aluminium projectiles bombarded onto the spacecraft structure. Of the remaining spacecraft #21, #26 and #28, one was given to Naval Post Graduate School and two went to the Applied Research Laboratory of the University of Texas, Austin. Of these three, one was destroyed in impact tests like spacecraft #22. The satellites launched in the 1985/88 period are sometimes referred to as Stacked Oscar On Scout (SOOS).
 |
| Image: Author's collection |
| NNSS-30010 (1964-063B) |
| Name | Intl. Designation | Launch | Re-entry | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NNSS-30010 | 1964-063B | 6-Oct-1964 | Also known as Ops-5798 | |
| NNSS-30020 | 1964-083D | 12-Dec-1964 | Also known as Ops-6582 | |
| NNSS-30030 | 1965-017A | 11-Mar-1965 | 14-Jun-1965 | Also known as Ops-7087 |
| NNSS-30040 | 1965-048A | 24-Jun-1965 | Also known as Ops-8480 | |
| NNSS-30050 | 1965-065F | 13-Aug-1965 | Also known as Ops-8464 | |
| NNSS-30060 | 1965-109A | 21-Dec-1965 | Also known as Ops-1509 | |
| NNSS-30070 | 1966-005A | 28-Jan-1966 | Also known as Ops-1593 | |
| NNSS-30080 | 1966-024A | 26-Mar-1966 | Also known as Ops-1117 | |
| NNSS-30090 | 1966-041A | 19-May-1966 | Also known as Ops-0082 | |
| NNSS-30100 | 1966-076A | 18-Aug-1966 | Also known as Ops-2366 | |
| NNSS-30110 | --- | --- | --- | Used as Transat |
| NNSS-30120 | 1967-034A | 14-Apr-1967 | Also known as Ops-0100 | |
| NNSS-30130 | 1967-048A | 18-May-1967 | Also known as Ops-7218 | |
| NNSS-30140 | 1967-092A | 25-Sep-1967 | Also known as Ops-4947 | |
| NNSS-30150 | --- | --- | --- | Used as P76-5 |
| NNSS-30160 | --- | --- | --- | Used as Hilat |
| NNSS-30170 | --- | --- | --- | Used as Polar Bear |
| NNSS-30180 | 1968-012A | 2-Mar-1968 | Also known as Ops-7034 | |
| NNSS-30190 | 1970-067A | 27-Aug-1970 | ||
| NNSS-30200 | 1973-081A | 30-Oct-1973 | ||
| NNSS-30210 | --- | --- | --- | Not used |
| NNSS-30220 | --- | --- | --- | Expended in tests, 1992 |
| NNSS-30230 | 1988-033A | 26-Apr-1988 | ||
| NNSS-30240 | 1985-066A | 3-Aug-1985 | ||
| NNSS-30250 | 1988-074A | 25-Aug-1988 | ||
| NNSS-30260 | --- | --- | --- | Not used |
| NNSS-30270 | 1987-080A | 16-Sep-1987 | ||
| NNSS-30280 | --- | --- | --- | Not used |
| NNSS-30290 | 1987-080B | 16-Sep-1987 | ||
| NNSS-30300 | 1985-066B | 3-Aug-1985 | ||
| NNSS-30310 | 1988-074B | 25-Aug-1988 | ||
| NNSS-30320 | 1988-033B | 26-Apr-1988 |
Launch dates of the NNSS series
Timation/NTS
The Timation or Navigation Technology Satellites (NTS) series tested new equipment to be used in the Global Positioning System (GPS). Timation-1 carried two high-precision quartz clocks for accurate measurements based on a three dimensional navigation technique. Timation-2 carried improved equipment and a dual frequency transmitter operating at 150/400 MHz. In addition Timation-3 or NTS-1 carried two rubidium vapor atomic clocks and operated at the 335 MHz and 1580 MHz frequencies whilst NTS-2 tested a ceasium clock. The satellite also carried an experimental solar array.
 |
| Image: Author's collection |
| Timation-1 (1967-053E) |
| Name | Intl. Designation | Launch | Re-entry | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Timation-1 | 1967-053E | 31-May-1967 | ||
| Timation-2 | 1969-082A | 30-Sep-1969 | 30-Oct-1970 | Also known as Ops-7613 |
| Timation-3 | 1974-054A | 14-Jul-1974 | Also known as NTS-1 and Ops-7518 | |
| NTS-2 | 1977-053A | 23-Jun-1977 |
Launch dates of the Timation/NTS series
TIP
The satellites in the Transit Improvement Program (TIP) were considered as a precursor to the Nova series and incorporated the Disturbance Compensating System (Discos), hence Transit Improved And Discos (Triad), which was designed to maintain position in orbit by correcting disturbances caused by solar wind and atmospheric resistance. In addition TIP-1 carried a radio-isotope thermal generator.
| Name | Intl. Designation | Launch | Re-entry | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TIP-1 | 1972-069A | 2-Sep-1972 | Also known as Triad | |
| TIP-2 | 1975-099A | 12-Oct-1975 | 26-May-1991 | |
| TIP-3 | 1976-089A | 1-Sep-1976 | 30-May-1981 |
Launch dates of the TIP series
Nova
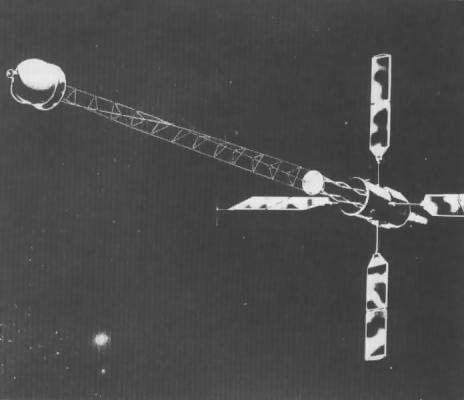
The Nova military navigational satellite had a mass of 166 kg and tested new instruments and techniques. They also carried a tri-axis vector magnetometer, four solar detectors and an internal mass displacement detector.
 |
| Image: Author's collection |
| Nova-1 (1981-044A) |
| Name | Intl. Designation | Launch | Re-entry | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nova-1 | 1981-044A | 15-May-1981 | Also known as NNSS 30480 | |
| Nova-2 | 1988-052A | 16-Jun-1988 | Also known as NNSS 30490 | |
| Nova-3 | 1984-110A | 12-Oct-1984 | Also known as NNSS 30450 |
Launch dates of the Nova series
Sources (for data after 2009)
[1] Wikipedia: GPS satellite blocks
[2] Gunter Krebs: Gunter's Space Page
Back to Directory of U.S. Military Rockets and Missiles, Appendix 3
Last Updated: 1 February 2024