Ball Aerospace LS-15 SBSS
The SBSS (Space Based Space Surveillance) program was initiated by the U.S. Air Force to provide a space-based infrastructure to detect and track objects in Earth orbit. Industry prime contractor was Northrop Grumman Mission Systems, and a sub-contract for a "pathfinder" SBSS satellite (a.k.a. SBSS-1) was awarded in 2004 to team led by Boeing, with Ball Aerospace being responsible for the satellite itself and its payload. The original plan called for a launch in 2007, and after some delay caused by problems with the Minotaur IV booster rocket, the SBSS-1 satellite was put into orbit on 26 September 2010.
The SBSS satellite has received the MDS designation LS-15A. It is equipped with a 30 cm telescope mounted on a two-axis gimbal, and orbits the Earth in a 630 km (390 miles) sun-synchronous orbit.
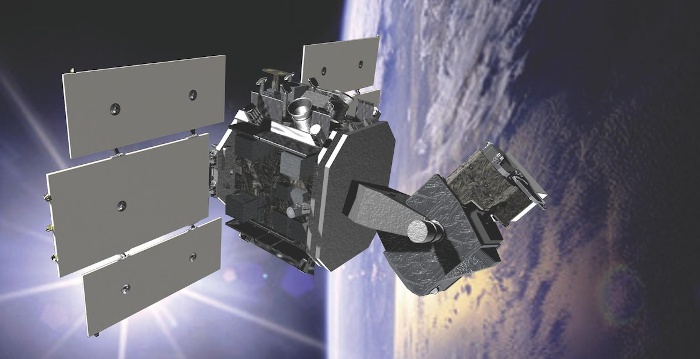 |
| Image: Boeing |
| LS-15A |
| Name | Intl. Designation | Launch | Re-entry | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SBSS-1 | 2010-048A | 26-Sep-2010 | Also known as USA-216 |
Launch dates of the SBSS series
Planned lifetime for the LS-15A was 7 years, but as of early 2024, it is still in active service. However, the majority of space-based space surveillance is currently handled by the GSSAP (Geosynchronous Space Situational Awareness Program) satellites.
Main Sources
[1] Wikipedia: Space Based Space Surveillance
[2] Gunter Krebs: SBSS 1
[3] USSF:
Space Based Space Surveillance
Back to Directory of U.S. Military Rockets and Missiles, Appendix 3
1 February 2024