E-Systems GQM-93
The USAF's Compass Dwell program was another early-1970s evaluation of potential high-altitude long-endurance RPVs, somewhat similar in purpose to the Compass Arrow (AQM-91 Firefly) and Compass Cope (YQM-94 B-Gull, YQM-98 R-Tern) programs. The goal of Compass Dwell was to develop an unmanned aircraft for data-gathering and as a communications relay with an endurance of at least 24 hours.
One of the competitors for Compass Dwell was E-Systems with its L450F aircraft. It was based on the Schweizer SGS 2-32 sailplane, and was first flown in manned configuration in February 1970. After having been converted to an unmanned vehicle, the L450F was evaluated by the USAF in early 1972 under the designation XQM-93A. Its competitor was the Martin Marietta Model 845A, which for unknown reasons did not receive any xQM missile designation.
 |
| Photo: Gil Bliss |
| L450F (XQM-93A in manned configuration) |
The modifications of the basic SGS 2-32, which were built into the L450F/XQM-93A, included a new Pratt & Whitney PT6A turboprop engine, a new fixed landing gear and of course new electronic equipment. The structure was also strengthened in some areas, and fin and rudder were of increased surface. The unmanned XQM-93A version replaced the pilot's bubble canopy with a flush fairing, and had a more advanced autopilot installed. The XQM-93A was controlled from the ground by a radio-command link, using telemetered flight data from the vehicle. The longest flight of the XQM-93A lasted more than 21 hours.
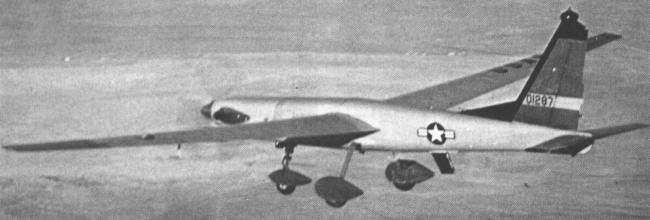 |
| Photo: USAF |
| XQM-93A |
The Compass Dwell evaluation program ended in 1972, but neither the XQM-93A nor the Martin Marietta 845A were selected for production. Long after program termination (at some time in the 1974/76 time frame) the designation of the unmanned L450F was formally changed to XGQM-93A.
Specifications
Note: Data given by several sources show slight variations. Figures given below may therefore be inaccurate!
Data for XQM-93A:
| Length | 9.02 m (29 ft 7 in) |
| Wingspan | 17.4 m (57 ft) |
| Height | 3.25 m (10 ft 8 in) |
| Weight | 2400 kg (5300 lb) |
| Speed | 370 km/h (200 kts) |
| Ceiling | > 15200 m (50000 ft) |
| Range | > 8300 km (4500 nm) |
| Endurance | > 24 hours |
| Propulsion | Pratt & Whitney Canada PT6A-34 turboprop; 354 ekW (475 ehp) |
Main Sources
[1] Kenneth Munson: "World Unmanned Aircraft", Jane's, 1988
Back to Current Designations Of U.S. Unmanned Military Aerospace Vehicles
Back to Directory of U.S. Military Rockets and Missiles
Last Updated: 29 December 2002