Northrop (Radioplane) AQM-38
In the late 1950's, Northrop's Radioplane division developed the RP-76 subscale radio-controlled recoverable target drone. The RP-76 was essentially the production version of the earlier RP-70, which had been evaluated by the U.S. Navy as the XKD4R-1 (q.v. for differences between the RP-70 and -76). Beginning in 1959, the RP-76 was used by the Army for surface-to-air missile training, mainly with the MIM-3 Nike-Ajax.
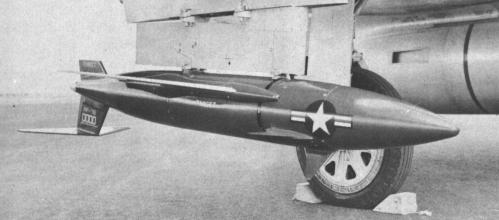 |
| Photo: via Ordway/Wakeford |
| AQM-38A |
The RP-76 was usually launched from USAF F-89 Scorpion aircraft, and was powered by an Aerojet solid-fuel rocket motor, which produced a thrust of 160 N (37 lb) for about 9 minutes. The drone had two rocket exhausts at the sides of the fuselage, and could reach a speed of Mach 0.94. The RP-76 was controlled in flight by an automatic control system with optional override by radio command, and could be recovered by a two-stage parachute system. The RP-76 had a unique set of flying surfaces, with 3 forward control fins, and a fixed horizontal tailplane located below the ventral vertical tail. Equipment included a Luneberg lens for radar reflectivity augmentation, and a Northrop RPTA-1 tracking aid system.
 |
| Photo: Western Museum of Flight |
| AQM-38A |
The Model RP-78 was the U.S. Navy's variant of the RP-76. It used a higher-thrust rocket motor, which allowed supersonic speeds of up to Mach 1.25. Other than most U.S. Naval drones before 1963, the RP-78 has apparently never received a KD type designation.
In June 1963, the RP-76 and RP-78 were designated as AQM-38A and AQM-38B, respectively. More then 2000 AQM-38 targets were built, and they were used until the mid-1970s.
Specifications
Note: Data given by several sources show slight variations. Figures given below may therefore be inaccurate!
Data for AQM-38A/B:
| AQM-38A | AQM-38B | |
|---|---|---|
| Length | 2.95 m (9 ft 8 in) | |
| Wingspan | 1.52 m (5 ft) | |
| Height | 0.46 m (1 ft 6.2 in) | |
| Diameter | 30 cm (12 in) | |
| Weight | 136 kg (300 lb) | |
| Speed | Mach 0.94 | Mach 1.25 |
| Ceiling | 18300 m (60000 ft) | 24000 m (78700 ft) |
| Endurance | 23 min. (powered: 9 min.) | |
| Range | ? | 70 km (44 miles) |
| Propulsion | Aerojet 530NS35 solid-fuel rocket; 160 N (37 lb) | Solid-fuel rocket; 440 N (100 lb) |
Main Sources
[1] Richard A. Botzum: "50 Years of Target Drone Aircraft", Northrop, 1985
[2] R.T. Pretty, D.H.R. Archer (eds.): "Jane's Weapon Systems 1970-71", McGraw-Hill, 1970
[3] Frederick I. Ordway III, Ronald C. Wakeford: "International Missile and Spacecraft Guide", McGraw-Hill, 1960
[4] Norman J. Bowman: "The Handbook of Rockets and Guided Missiles", Perastadion Press, 1963
Back to Current Designations Of U.S. Unmanned Military Aerospace Vehicles
Back to Directory of U.S. Military Rockets and Missiles
Last Updated: 30 March 2003