Raytheon AGM-181 LRSO
The LRSO (Long-Range Standoff) cruise missile program was initiated by the U.S. Air Force in 2015 to develop a replacement for the AGM-86B ALCM. Two competitors, Lockheed Martin and Raytheon, received development contracts for the LRSO missile in August 2017. Earlier, the designations YAGM-180A (Lockheed Martin) and YAGM-181A (Raytheon) had been allocated for LRSO.
In 2020, it was announced that the LRSO program would continue with Raytheon as the only contractor, and in 2021, the company was awarded an EMD (Engineering and Manufacturing Development) contract for the AGM-181 missile. Current plans call for a production decision in 2027, and an initial operational capability around 2030. The USAF plans to procure around 1000 missiles. The AGM-181 had completed at least 9 successful flight tests by the end of 2022.
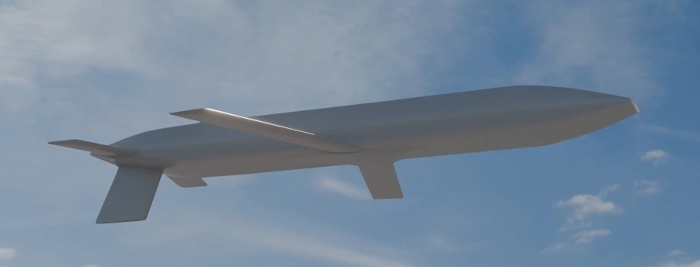 |
| Image: USAF |
| AGM-181A |
Launch platforms for the AGM-181 will be the B-52J and B-21A bombers, and the stand-off range is expected to be more than 2500 km (1500 miles). According to USAF nomenclature records, the AGM-181A production version is powered by a single Williams F107-WI-106 turbofan. The only warhead option will be the W80-4 thermonuclear warhead (a life-extended W80-1) of unspecified yield.
Specifications
No details about the characteristics of the AGM-181 missile are available.
Main Sources
[1] Wikipedia: AGM-181 LRSO
[2] Air & Space Forces Magazine:
LRSO Stealth Nuclear Missile
On Track for Production Decision in 2027
[3] Air & Space Forces Magazine:
New Details
of Secret LRSO Missile: Nine Successful Flight Tests in 2022
Back to Current Designations Of U.S. Unmanned Military Aerospace Vehicles
Back to Directory of U.S. Military Rockets and Missiles
Last Updated: 12 June 2025